In the realm of chronic illnesses, few are as pervasive and demanding as diabetes. With millions of individuals worldwide grappling with this metabolic disorder, the need for effective management tools has never been more pressing. Among the arsenal of resources available to diabetics, the blood sugar monitor stands as a beacon of hope and control. In this article, we delve into the significance of blood sugar monitors , their types, and the pivotal role they play in diabetes management.
Understanding Blood Sugar Monitoring
Blood sugar, or glucose, is the primary source of energy for the body's cells. However, in diabetes, the body either does not produce enough insulin (Type 1 diabetes) or cannot effectively use the insulin it produces (Type 2 diabetes). This leads to elevated levels of glucose in the blood, which, if left uncontrolled, can result in severe complications such as cardiovascular disease, kidney failure, and nerve damage.
Monitoring blood sugar levels is a cornerstone of diabetes management. By regularly measuring glucose levels, individuals can make informed decisions about medication, diet, and lifestyle choices to keep their blood sugar within a target range. This is where blood sugar monitors , also known as glucometers, come into play.
Types of Blood Sugar Monitors
Blood sugar monitors are available in various forms, ranging from traditional fingerstick glucometers to continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) systems. Each type offers unique benefits tailored to different user preferences and needs.
- Traditional Fingerstick Glucometers: These portable devices require a small drop of blood, usually obtained by pricking the fingertip with a lancet. The blood sample is then applied to a test strip inserted into the meter, which analyzes the glucose level and displays the result within seconds. While traditional glucometers provide accurate readings, they offer point-in-time measurements and may not capture fluctuations between tests.
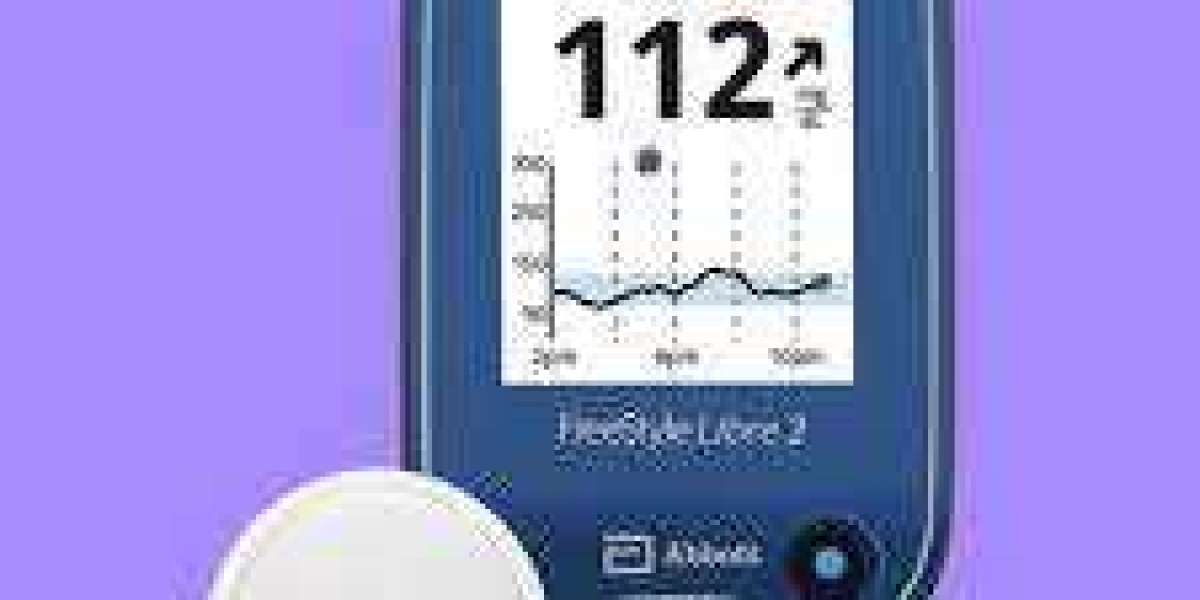
- Continuous Glucose Monitoring (CGM) Systems: CGM systems utilize a sensor inserted under the skin to continuously monitor glucose levels in the interstitial fluid. blood sugar monitors These sensors measure glucose levels every few minutes, providing real-time data on trends and fluctuations throughout the day and night. CGM systems offer a more comprehensive view of blood sugar dynamics, allowing users to spot patterns and make timely adjustments to their diabetes management regimen.
- Flash Glucose Monitoring: A newer addition to the market, flash glucose monitoring systems provide on-demand glucose readings without the need for routine fingerstick calibrations. Users wear a small sensor on the skin, and by scanning the sensor with a reader or smartphone, they can obtain current glucose levels along with historical data trends.