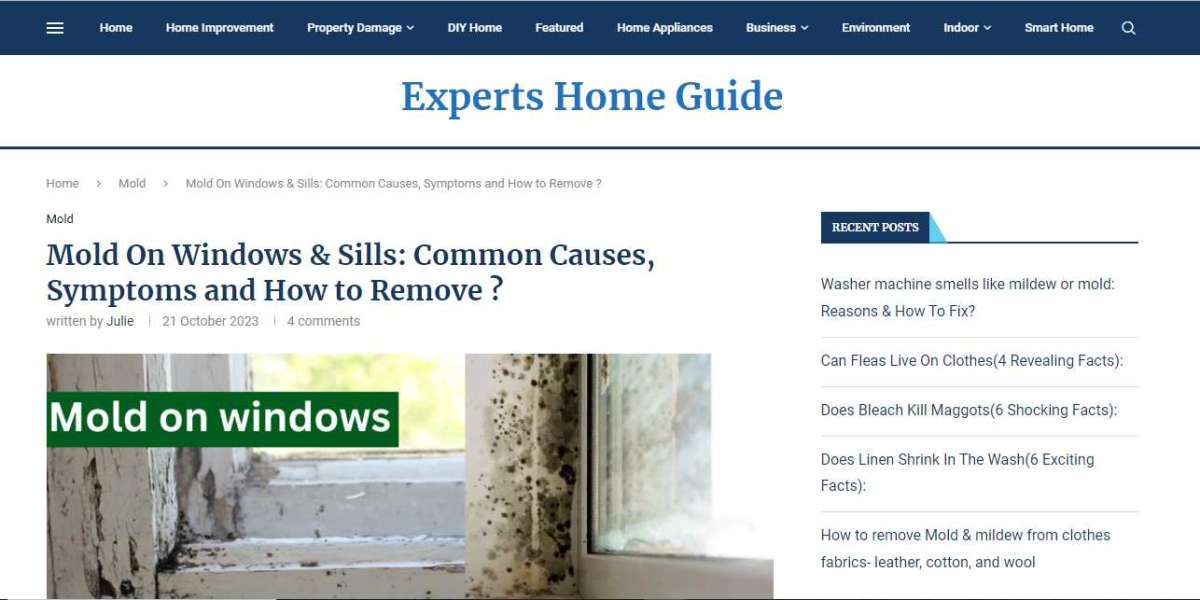
Introduction
Mold growth on windows can be a common issue in many households and commercial buildings. While it may seem like a minor inconvenience, mold poses significant risks to both property and health. In this comprehensive guide mold on windows , we will delve into the causes of mold on windows, the associated risks, and effective remediation strategies to eliminate this problem.
Causes of Mold on Windows
High Humidity Levels
One of the primary causes of mold growth on windows is high humidity levels within the indoor environment. When warm, moist air comes into contact with cooler window surfaces, condensation occurs, creating an ideal environment for mold spores to thrive.
Poor Ventilation
Inadequate ventilation exacerbates humidity levels, leading to moisture accumulation on windows. Poorly ventilated areas such as bathrooms, kitchens, and basements are particularly prone to mold growth.
Water Intrusion
Leaky windows or damaged seals allow water to penetrate into the interior spaces, promoting mold growth. Over time, unnoticed water intrusion can result in extensive mold colonies forming on window frames and sills.
Organic Matter Accumulation
Dust, dirt, and other organic matter accumulate on window surfaces, providing nutrients for mold growth. Neglected cleaning routines contribute to the buildup of these substances, further fostering mold development.
Risks Associated with Mold on Windows
Property Damage
Mold colonization on windows can lead to structural damage, compromising the integrity of the window frames and sills. Additionally, prolonged exposure to moisture may result in wood rot and decay, necessitating costly repairs or replacements.
Health Impacts
Exposure to mold spores can trigger allergic reactions and exacerbate respiratory conditions such as asthma and bronchitis. Individuals with compromised immune systems are particularly vulnerable to the adverse health effects of mold exposure, including respiratory infections and systemic inflammation.
Indoor Air Quality
Mold infestations on windows contribute to poor indoor air quality, as airborne spores circulate throughout the living or working spaces. Persistent exposure to mold-contaminated air can lead to chronic respiratory issues and exacerbate existing health conditions.
Remediation Strategies
Improve Ventilation
Enhancing ventilation in areas prone to mold growth, such as bathrooms and kitchens, helps reduce humidity levels and prevent condensation on windows. Install exhaust fans and open windows periodically to facilitate air circulation and moisture removal.
Address Water Intrusion
Inspect windows regularly for signs of water intrusion, such as leaks or condensation buildup. Repair damaged seals, caulking, or weather stripping to prevent water from entering the interior spaces and creating conducive conditions for mold growth.
Clean and Maintain Windows
Regularly clean window surfaces to remove accumulated dirt, dust, and organic matter that serve as mold nutrients. Use mild detergent solutions or specialized mold cleaners to disinfect and sanitize window frames, sills, and glass panes.
Use Dehumidifiers
Employ dehumidifiers in areas with elevated humidity levels to extract excess moisture from the air, reducing the risk of mold growth on windows. Maintain optimal indoor humidity levels (ideally between 30% to 50%) to inhibit mold proliferation and maintain a healthy indoor environment.