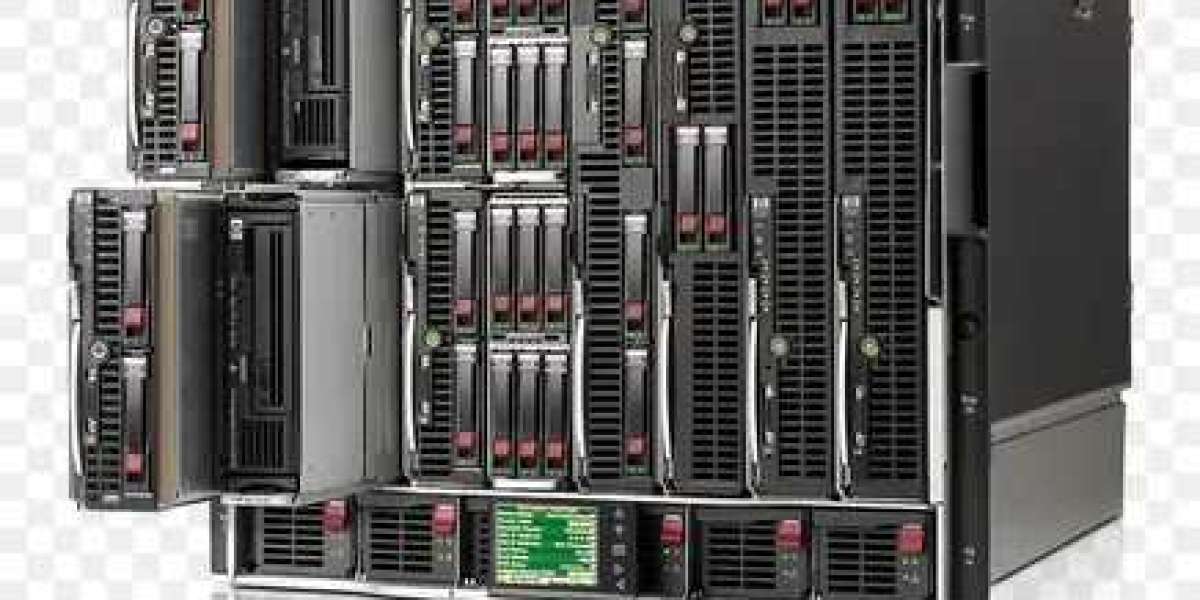
As data centers continue to expand to accommodate growing demands, finding solutions that save space and energy becomes increasingly critical.
One such solution gaining popularity is the adoption of blade servers. These compact and energy-efficient devices offer a multitude of benefits, revolutionizing the way data centers operate.
In this article, we explore how blade-type servers can transform your data center, maximizing space utilization and minimizing energy consumption.
Streamlined Infrastructure
These servers pack a powerful punch in a compact form factor. Unlike traditional rack-mounted servers, which occupy significant space, these servers consolidate computing resources into a smaller footprint.
- Simplified Cabling
Traditional servers require extensive cabling, resulting in a tangled web of wires that complicates maintenance and airflow management.
In contrast, these servers feature a unified infrastructure with shared components, reducing the complexity of cabling. This streamlined design not only enhances airflow for improved cooling efficiency but also facilitates easier troubleshooting and upgrades.
- Scalability:
The modular nature of these servers allows for seamless scalability to meet evolving business needs.
Data center administrators can easily add or remove blade modules as required without disrupting existing operations. This flexibility enables organizations to adapt swiftly to changing workloads and demands, optimizing resource utilization and minimizing waste.
Enhanced energy efficiency
These servers optimize energy consumption by consolidating power and cooling resources. With shared power supplies and cooling fans, these servers operate more efficiently than their rack-mounted counterparts.
- Dynamic Power Management:
These modern servers are equipped with advanced power management features that intelligently regulate energy usage based on workload demands.
Through techniques such as dynamic voltage and frequency scaling, these servers adjust power levels in real time to match processing requirements, minimizing idle power consumption without compromising performance.
- Virtualization Support:
These servers are well-suited for virtualized environments, where multiple virtual machines (VMs) run concurrently on a single physical server. By consolidating workloads onto fewer physical servers, virtualization reduces the overall energy footprint of the data center.
These servers excel in virtualized environments due to their high-density design and robust management capabilities, enabling data center operators to achieve higher levels of resource utilization and energy efficiency.
Simplified Management and Maintenance
These servers streamline management tasks through centralized management interfaces. Administrators can monitor and control multiple blade modules from a single management console, simplifying day-to-day operations and reducing management overhead.
- Hot-Swap Capabilities:
Blade devices feature hot-swappable components that facilitate non-disruptive maintenance and upgrades. Administrators can replace faulty components or upgrade hardware modules without shutting down the entire server chassis, minimizing downtime and ensuring continuous service availability.
This hot-swap capability enhances system reliability and simplifies maintenance procedures, reducing operational risks for data center operators.
- Integrated Management Tools:
Many server systems come equipped with integrated management tools that automate routine tasks and streamline administrative workflows. These tools provide insights into system health, performance metrics, and resource utilization, empowering administrators to make informed decisions and optimize server operations.
By automating repetitive tasks and providing comprehensive monitoring capabilities, integrated management tools enhance operational efficiency and reduce the burden on IT staff.
Improved Performance and Resource Utilization
These servers are engineered for high-density computing, allowing data centers to maximize resource utilization within limited physical space. With multiple blade modules housed in a single chassis, these servers achieve higher compute density compared to traditional rack-mounted servers.
This compact design enables data centers to support more workloads and applications within the same footprint, effectively leveraging available resources to enhance overall performance.
- Resource Pooling:
These servers facilitate resource pooling, enabling data center operators to dynamically allocate computing resources based on workload demands. Through virtualization and resource management software, administrators can create resource pools comprising CPU, memory, and storage resources from multiple blade modules.
This pooling mechanism enhances resource utilization and enables efficient workload provisioning, ensuring optimal performance for diverse workloads without overprovisioning or underutilization.
- Fault Tolerance:
These servers offer built-in fault tolerance mechanisms that enhance system reliability and availability. Redundant components, such as power supplies and network interfaces, ensure continued operation in the event of hardware failures.
Additionally, blade architectures support technologies like RAID (Redundant Array of Independent Disks) for data redundancy and fault tolerance, safeguarding critical data against disk failures. These fault-tolerant features minimize service disruptions and downtime, ensuring uninterrupted operations for mission-critical applications.
Cost savings and return on investment (ROI)
These servers can result in significant cost savings by reducing capital expenditures associated with hardware acquisition and infrastructure expansion. The high-density design of these servers allows data centers to achieve greater computing capacity using fewer physical servers, thereby lowering upfront hardware costs. Additionally, the compact footprint of these servers reduces space requirements, resulting in savings on real estate and facility expenses.
Operational Efficiency:
These servers contribute to operational efficiency by streamlining management processes, reducing energy consumption, and minimizing downtime. Centralized management interfaces and integrated management tools simplify administrative tasks, freeing up IT resources for higher-value activities.
Moreover, the energy-efficient design of blade servers leads to lower ongoing operational costs, including electricity bills and cooling expenses. By minimizing downtime through fault tolerance and hot-swap capabilities, blade servers help maximize productivity and revenue generation, delivering a tangible return on investment for data center operators.
- Scalability and Future-Proofing:
Blade servers offer scalability and future-proofing capabilities that enable data centers to adapt to evolving business requirements and technological advancements. The modular architecture of blade servers allows for seamless scalability, enabling data centers to expand capacity as needed without overhauling existing infrastructure.
Furthermore, blade servers are designed to support emerging technologies such as high-performance computing (HPC), artificial intelligence (AI), and edge computing, ensuring compatibility with future workloads and applications.
Conclusion
In an era where efficiency and sustainability are paramount, blade servers offer a compelling solution for data centers seeking to maximize space utilization and minimize energy consumption. By streamlining infrastructure, enhancing energy efficiency, and simplifying management and maintenance, blade servers enable data center operators to achieve higher levels of performance and reliability while reducing operational costs and environmental impact. As organizations continue to prioritize efficiency and agility in their data center operations, blade servers are poised to play a central role in shaping the future of data management.